Causes of conflicts in a team: how to identify sources of tension and neutralize them
Conflicts are a natural part of teamwork and can arise even in the most well-organized groups. The causes of team conflicts vary—from communication differences to conflicting goals and personalities. Identifying the sources of conflict is key to effectively neutralizing them, and understanding team dynamics makes it easier to apply appropriate resolution strategies. This article explores the main causes of workplace conflicts, provides examples, and explains how the DISC tool can help better understand different personality styles and manage tensions.
1. Differences in communication styles
One of the primary sources of tension in teams is differences in communication. Variations in how people express their thoughts, the level of formality they use, and the speed at which they share information can lead to misunderstandings and frustration. For example, a direct communicator might clash with someone who prefers a more measured and diplomatic approach, leading to conflict.
Using DISC to understand communication styles
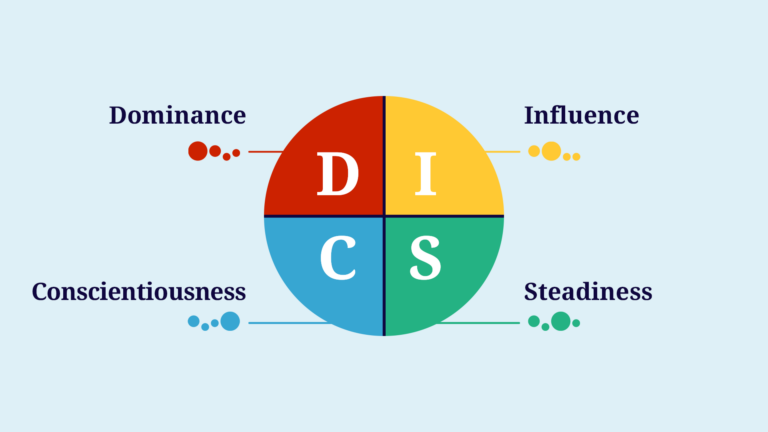
The DISC tool helps identify individual communication styles within a team, making it easier to address personality-based conflicts. DISC categorizes personalities into four types: Dominant, Influential, Steady, and Conscientious.
- A Dominant person, who values speed and clarity, might find it difficult to work with a Steady individual, who prefers a more deliberate pace.
- Influential people focus on interpersonal relationships and may struggle with Conscientious colleagues who prioritize precision and data.
Recognizing these differences allows teams to adjust their communication styles, reducing misunderstandings.
2. Conflicting goals and priorities
Another common source of tension is misaligned goals and priorities. Each team member may have a different focus or responsibility, which can lead to conflicts of interest.
Example: The marketing department may prioritize building the company’s brand, while the sales team focuses on immediate revenue generation. These conflicting objectives can create friction between teams.
Neutralizing the conflict
To avoid such tensions, teams should regularly clarify shared goals and objectives and ensure alignment across departments. Managers should establish clear priorities and reinforce them consistently to prevent misunderstandings. Transparent communication helps adjust priorities and prevents unnecessary escalation.
3. Unequal workload and resource distribution
Imbalances in workload or access to resources are another common cause of workplace conflict. A situation where one employee is overwhelmed with tasks while another has fewer responsibilities can lead to resentment and lower team morale.
Example of conflict resolution
A proactive approach includes:
- Regularly reviewing workload distribution.
- Holding feedback sessions where team members discuss their workload openly.
- Ensuring transparent task allocation to foster fairness and collaboration.
4. Differences in values and work approach
Conflicts may also arise from diverging values and attitudes toward work. Some employees may prioritize innovation and creativity, while others may value stability and structure.
How to prevent such conflicts?
Building a strong team culture with clearly defined shared values helps prevent friction caused by differing perspectives. Team-building activities and fostering an open dialogue about work styles can improve mutual understanding and enhance collaboration.
5. Unclear roles and responsibilities
A lack of clearly defined roles and responsibilities is a frequent cause of confusion and frustration in teams. When employees are unsure about their specific duties, conflicts may arise over task ownership and accountability.
How to avoid role-related conflicts?
- Conduct regular team meetings to discuss role expectations.
- Define clear responsibilities for each position.
- Ensure that task delegation aligns with employee strengths and skills.
6. Insufficient communication
Poor communication is one of the most common causes of workplace conflict. Lack of regular meetings, unclear messaging, and inconsistent feedback can lead to misinterpretations and misalignment.
Neutralizing communication gaps
- Establish scheduled team meetings to ensure consistent information sharing.
- Use team collaboration tools (e.g., Slack, Asana, Microsoft Teams) to streamline communication.
- Encourage an open-door policy, where employees can freely express concerns.
7. Differences in work styles
Varying approaches to time management, task execution, and decision-making can lead to tensions. A fast-paced, high-energy employee may struggle to collaborate with a detail-oriented, methodical coworker.
Resolving work style differences using DISC
DISC helps identify different work styles and allows managers to assign tasks accordingly:
- Dominant individuals thrive in fast-moving projects that require quick decision-making.
- Steady personalities excel in structured, predictable environments.
- Conscientious employees perform best in detail-heavy, analytical tasks.
Understanding these differences enables better collaboration and reduces work style-related conflicts.
8. Hierarchical and competency differences
Workplace hierarchy and skill gaps can also contribute to conflicts, especially when junior employees feel overlooked or lack opportunities to express their ideas.
How to manage hierarchy-related conflicts?
- Implement regular team check-ins, where all members have a voice.
- Provide opportunities for cross-functional collaboration and mentorship programs.
- Foster an inclusive culture where contributions are valued, regardless of seniority.
Conclusion
The causes of team conflicts can stem from communication gaps, differing work styles, unclear roles, or competing priorities. The DISC tool is a valuable resource for identifying personality-based differences that may contribute to tension and adjusting communication strategies accordingly.
By recognizing conflict sources early and applying appropriate resolution strategies, teams can prevent escalations and foster an environment of trust and collaboration.